(Translated By Adrian Chan-Wyles PhD)
Translator’s Note: I have written before on the many and impressive Soviet successes achieved during to the so-called “Space Race” with a capitalist US that cared nothing about humanity and everything about monetary profit. Indeed, where NASA failed to design and send probes to Venus – the Soviets were extraordinarily successful. In 1982, the “Venera-13” probe landed successfully on the surface of Venus, and took compelling images that may have recorded “life”. The 1972 probe described below – was the back-up component of the successful “Venera-8” Soviet Mission (renamed “Kosmos-482” after its launch failure). In other words, the primary “Venera-8” mission was a success – but its back-up module failed to reach its destination. The Soviet Space Programme had a tendency to send probes in supportive “pairs” (known as “Space Communism”). As the USSR was not interested in – or limited by – financial cost, the progressive technology generated through the use of Marxist-Leninist dialectics did not possess any material limitations premised upon monetary “profit”. Of course, modern Russia is “capitalist” and has not been able to replicate the innovation that came out of the Stalinist-era and the Soviet victory during WWII. Although the returning Soviet probe was launched in 1972 – the attitude is that “capitalist” Russia, if it had been able to retrieve the fallen probe, might well had benefitted from its decades-old technology! If you “click” on the link above – you will find my articles about the possibility that the Soviets discovered “life” on Venus! ACW (10.5.2025)
The Soviet-era probe designated – Kosmos-482 – sank into the Indian Ocean, West of Jakarta, after a controlled descent from Earth’s orbit. It was launched in 1972, but due to a malfunction, it remained in a high elliptical orbit for over 50-years.
The Soviet Kosmos-482 probe, launched in 1972, fell into the Indian Ocean, Roscosmos said. The descent of the device from orbit was controlled by the Automated Warning System for Dangerous Situations in Near-Earth Space.
“The Kosmos-482 probe has returned to Earth and ceased to exist – after leaving orbit – and falling in the Indian Ocean,” the Russian State Corporation stated:
“The Kosmos-482 spacecraft left orbit and fell into the ocean
Launched in 1972, the Kosmos-482 spacecraft ceased to exist, falling out of orbit and crashing into the Indian Ocean
The descent of the apparatus was controlled by the Automated Warning System for Hazardous Situations in Near-Earth Space.
According to calculations by specialists from TsNIIMash (part of Roscosmos), the device entered the dense layers of the atmosphere at 9:24 Moscow time, 560 km west of Middle Andaman Island, and fell in the Indian Ocean west of Jakarta.
The spacecraft was launched in the spring of 1972 to study Venus, but due to a malfunction in the booster-engine, it remained in a high elliptical orbit of the Earth, gradually re-approaching the planet.”
It entered the dense layers of the atmosphere at 9:24 Moscow time, 560 km West of the island of Middle Andaman and fell in the ocean West of the capital of Indonesia, Jakarta.
The probe was launched in 1972 to explore Venus, but due to a malfunction of the upper launch-stage, it remained in the high elliptical orbit of the Earth – and has gradually re-approached the surface of the planet – slowly but surely ever-since..
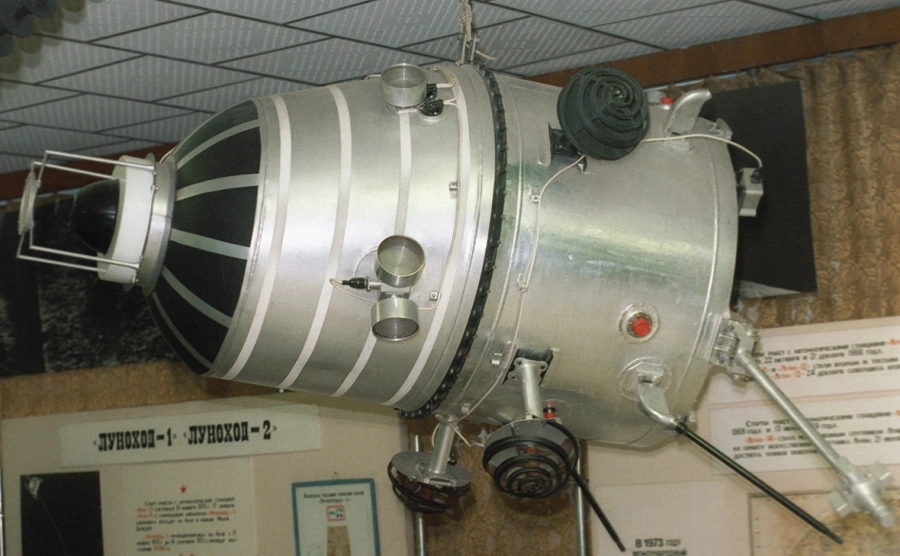
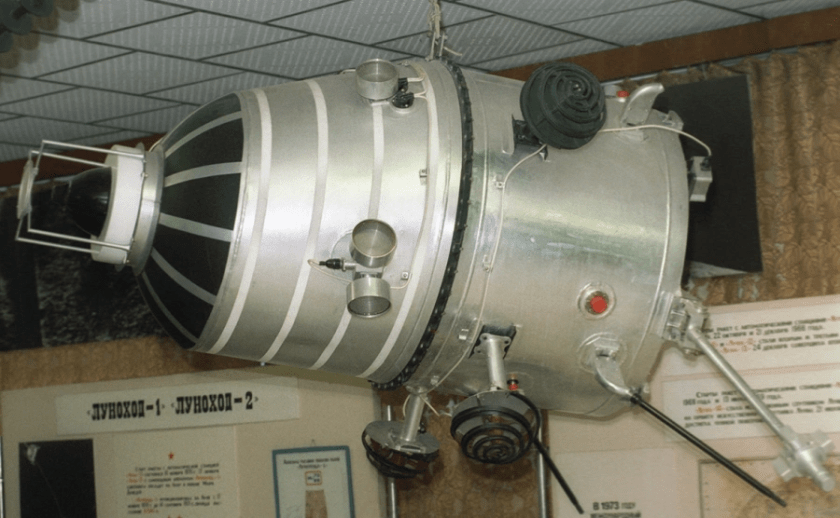
Kosmos-482 was launched by the Soviet Union using the Molniya-M Launch Vehicle as part of the outstanding Venus Exploration Programme. The device was almost identical to the Venera-8 Station (which successfully reach Venus) and was intended as a back-up device to study the atmosphere and surface of that planet. After the launch failure – the probe broke up into several parts. The main body of the probe burned-up in the atmosphere during in 1981 – but the descent vehicle remained in orbit and circled the Earth for more than 50 years.
In the Spring of 2025, the Kosmos-482 Descent Vehicle began its final descent.
Russian Language Text:
https://www.rbc.ru/society/10/05/2025/681f1a3c9a79474e4e0e904f
В Индийский океан упал запущенный СССР аппарат для исследования Венеры
Общество , 10 мая, 2025 12:22
В Индийский океан упал советский аппарат «Космос-482» для исследования Венеры
Советский аппарат «Космос-482» затонул в Индийском океане к Западу от Джакарты после контролируемого схождения с орбиты. Его запустили в 1972 году, однако из-за неисправности он остался на высокой эллиптической орбите
В Индийский океан упал запущенный в 1972 году советский аппарат «Космос-482», сообщил Роскосмос. Схождение аппарата с орбиты контролировала Автоматизированная система предупреждения об опасных ситуациях в околоземном космическом пространстве.
«Космический аппарат «Космос-482» прекратил существование, сойдя с орбиты и упав в Индийском океане», — рассказали в госкорпорации. Он вошел в плотные слои атмосферы в 9:24 мск в 560 км западнее острова Средний Андаман и упал в океане к западу от столицы Индонезии Джакарты.
Аппарат запустили в 1972 году для исследования Венеры, однако из-за неисправности разгонного блока он остался на высокой эллиптической орбите Земли и постепенно приближался к планете.
«Космос-482» был запущен Советским Союзом с помощью ракеты-носителя «Молния-М» в рамках программы по исследованию Венеры. Аппарат был практически идентичен станции «Венера-8» и предназначался для изучения атмосферы и поверхности планеты. После запуска аппарат распался на несколько частей. Основной корпус зонда сгорел в атмосфере еще в 1981 году, однако спускаемый аппарат остался на орбите и более 50 лет вращался вокруг Земли.
Весной 2025 года спускаемый аппарат «Космос-482» начал снижение.
https://t.me/roscosmos_gk/17407
🔴Аппарат «Космос-482» сошел с орбиты и упал в океан
Запущенный в 1972 году космический аппарат «Космос-482» прекратил существование, сойдя с орбиты и упав в Индийском океане
Схождение аппарата контролировалось средствами Автоматизированной системы предупреждения об опасных ситуациях в околоземном космическом пространстве.
В соответствии с расчетами специалистов ЦНИИмаш (входит в Роскосмос), аппарат вошел в плотные слои атмосферы в 9:24 мск в 560 км западнее острова Средний Андаман и упал в Индийском океане западнее Джакарты.
Аппарат был запущен весной 1972 года для исследования Венеры, однако из-за неисправности разгонного блока остался на высокой эллиптической орбите Земли, постепенно приближаясь к планете.